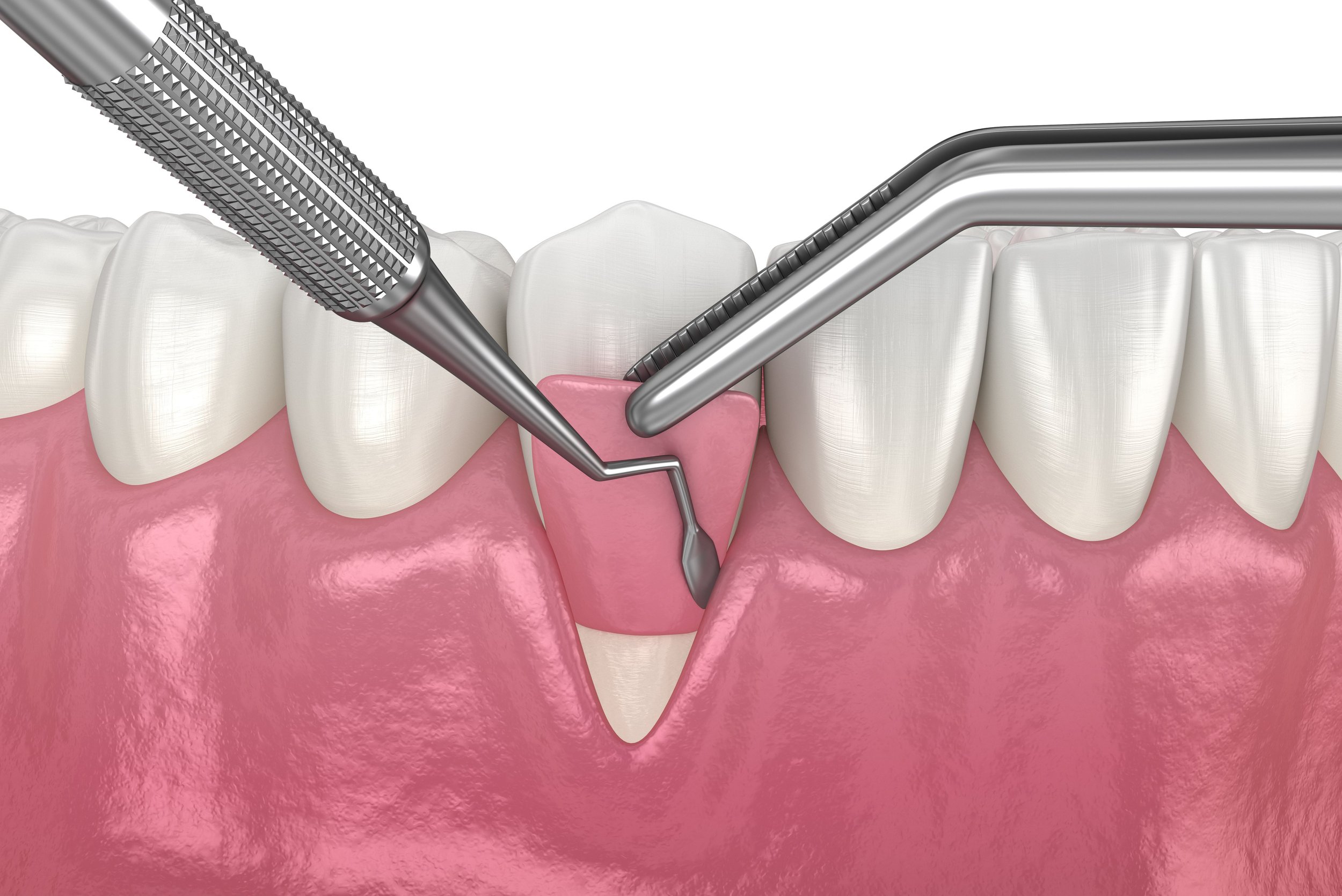
GINGIVAL GRAFT
Gingival Graft For Gum Recession
Gum recession is a common dental concern that not only affects the aesthetics of your smile but also poses risks to your oral health. When gums recede, they expose the sensitive root surfaces of your teeth, making them susceptible to discomfort and potential damage.
Gingival grafts are similar to connective tissue grafts in that both procedures involve using tissue from the roof of the mouth. However, in contrast to creating a flap and extracting tissue from beneath the top layer of tissue, free gingival grafts involve taking a small amount of tissue directly from the roof of the mouth and attaching it to the area of the gums that needs treatment.
This technique is commonly used for individuals with naturally thin gums who need additional tissue to increase their gum volume.
Gingival Graft
Reasons for Gum Recession
1. Periodontal Disease
Periodontal diseases like gingivitis and periodontitis can cause gum recession. These conditions result from the buildup of plaque and bacteria, leading to inflammation and gum tissue damage.
2. Aggressive Brushing
Overzealous brushing with a hard-bristle toothbrush can erode gum tissue, contributing to gum recession over time.
3. Genetics
Genetic factors can make some individuals more susceptible to gum recession, even with excellent oral hygiene habits.
Benefits of Gingival Graft Surgery
Gingival graft surgery offers a range of benefits, including:
1. Improved Aesthetics
Gum grafting can enhance the appearance of your smile by restoring a balanced gum line.
2. Reduced Sensitivity
The procedure can alleviate tooth sensitivity by covering exposed root surfaces.
3. Gum Health Restoration
Gingival graft surgery promotes gum tissue regeneration and overall gum health improvement.
There are several types of gum grafts, each with specific advantages. These include:
1. Connective Tissue Graft
This is the most common type, where a small incision is made in the roof of your mouth, and a graft is taken from underneath the surface. It's then placed over the affected area.
2. Graft of The Free Gingival Margin
In this method, tissue is directly taken from the roof of the mouth and placed on the recipient site. It's often used for patients with thin gums.
3. Pedicle Graft
In this technique, the graft is taken from an adjacent gum tissue and then stretched over the exposed area, avoiding the need for incisions in the palate.
Types of Gingival Grafts
Gingival Graft Procedure
1. Consultation
Before the surgery, you'll have a consultation with your periodontist to discuss the procedure, expectations, and any concerns you may have.
2. Anesthesia
Local anesthesia is administered to ensure a pain-free experience during the surgery.
3. Graft Harvesting
Depending on the type of graft, the tissue is harvested from the roof of your mouth or an adjacent area.
4. Graft Placement
The graft is then carefully placed and sutured in position to cover the exposed root surfaces.
5. Post-Surgery Care
Your periodontist will provide detailed aftercare instructions to ensure a smooth recovery process.
Recovery and Aftercare
The success of your gingival graft surgery largely depends on proper aftercare. Follow these essential guidelines:
Maintain good oral hygiene.
Avoid aggressive brushing.
Follow your dentist's post-surgery instructions.
Attend follow-up appointments for monitoring.
Gingival graft surgery is a valuable dental procedure that can significantly improve your oral health and aesthetics. If you're experiencing gum recession or related issues, consult with a skilled periodontist to discuss your options.
Remember, your oral health is a crucial part of your overall well-being, and gingival graft surgery can be a game-changer in your journey to a healthier, more confident smile.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
During the surgery, local anesthesia is administered, ensuring that you do not feel pain. Some discomfort and mild swelling may occur after the procedure, but this can be managed with pain relief medication.
-
The recovery period can vary from person to person, but it typically takes a few weeks for the surgical site to heal completely. Your periodontist will provide specific aftercare instructions to help facilitate a smooth recovery.
-
As with any surgical procedure, there are some risks, including infection, bleeding, or graft failure. However, these risks are minimal when the procedure is performed by a skilled periodontist and proper aftercare is followed.
-
Yes, the goal of the surgery is to achieve a natural-looking and balanced gum line. Your periodontist will work to ensure that the grafted tissue blends seamlessly with your existing gums.



